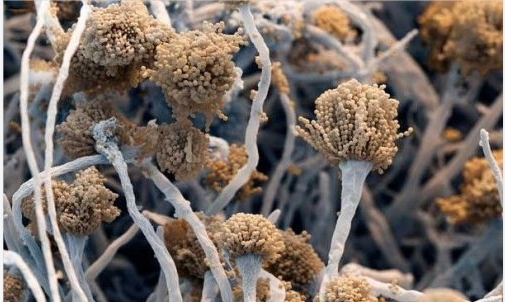
Aspergillus fumigatus
Aspergillus fumigatus is a group of Aspergillus, also known as anti-amoeba drug. It is a white crystalline solid composed of C, H and O, which belongs to organic acid substances. It is an effective fungal metabolite isolated from Aspergillus fumigatus. It can be used as a natural insoluble antibiotic to control fungal diseases caused by bee microsporidia. This group of Aspergillus is fluffy or flocculent, spreading. Dark green, smoke green, old colonies are darker. The reverse side has the same color. The conidia head is columnar, green when young, and dark green to dark brown or coal when mature. The conidial peduncle is short, smooth and often green. The top capsule bottle is a thermophilic mold and can adapt to a wide range of temperatures. The minimum growth temperature is 10 ℃ - 12 ℃, the best is 37 ℃ - 45 ℃, and the maximum is 57 ℃ - 58 ℃; The lethal temperature of nutrient mycelium is above 60 ℃. The minimum relative humidity for spore germination is 86%, and the asexual reproduction must be 90%. In the middle and late stages of grain fever and mildew, it often occurs in large quantities, which promotes the rise of grain temperature and the deterioration of grain. At the same time, it can cause diseases to poultry and other vertebrates (including humans), and is the pathogen causing "aspergillosis". Some strains can produce toxins and cause animal poisoning.
Research progress
It was first isolated from a specific strain of Aspergillus H-3 in 1949, which was later named Aspergillus fumigatus. Because of its remarkable effect in the prevention and treatment of microsporidiosis, it has been used as an antibiotic for the treatment of this disease. Nicotinamycin can also effectively inhibit angiogenesis. Because of its huge potential medical value, the biological activity of nicotinamycin and its synthetic derivatives has become a hot topic. It is derived from several derivatives of nicotinamycin skeleton, which can inhibit the growth and cytotoxicity of endothelial cells in vivo and in vitro, and is used to treat a variety of cancers, and has a certain role in the treatment of cancer, weight loss and other aspects. However, China has not authorized the use of nicotinic drugs, and the research on the synthesis of related drugs is relatively small, and there are few relevant references. Therefore, the research on fumatoxin and its derivatives is of great value.
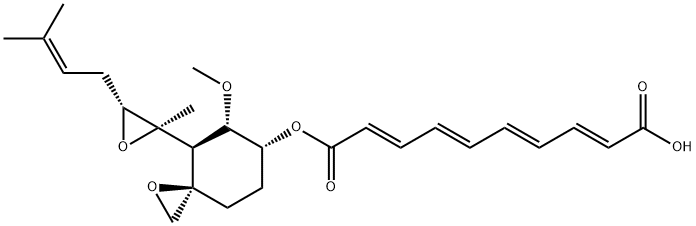
Chinese name: Aspergillus fumigatus
English name: Fumagillin
CAS:23110-15-8
Molecular formula: C26H34O7
Molecular weight: 458.5
DWRIVATIVE
Nicotinamycin derivative
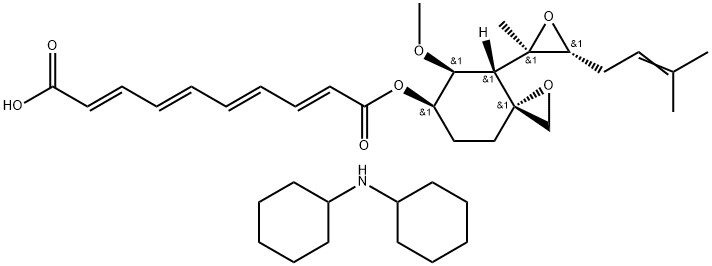
Chinese name: Fumaricin B
English name: Bicyclohexylammonium fumagillin
CAS:41567-78-6
Molecular formula: C38H57NO7
Molecular weight: 639.87
In clinical application, it can be used to treat intestinal amoebiasis caused by AIDS and other immune defects.
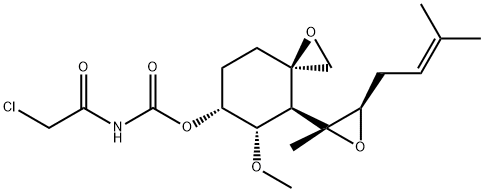
Chinese name: O - (chloroacetylcarbamoyl) nicotinol
English name: AGM-1470
CAS:129298-91-5
Molecular formula: C19H28ClNO6
Molecular weight: 401.88
It has a strong effect of inhibiting angiogenesis, and has fewer toxic and side effects in vivo. However, the mechanism of its action on endothelial cells is still unclear.
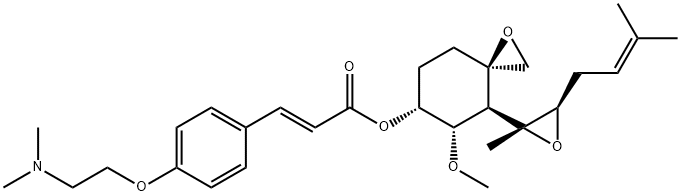
Chinese name: Bironibu
English name: Beloranib
CAS:251111-30-5
Molecular formula: C29H41NO6
Molecular weight: 499.64
The compound has anti-angiogenic activity in tumor treatment. At the same time, it also plays a certain role in weight loss and cardiovascular, central nervous and respiratory diseases.
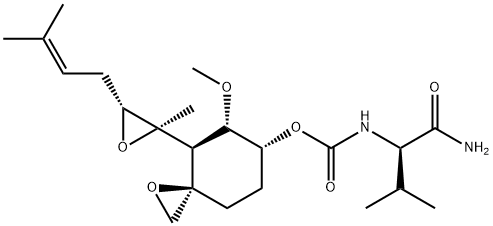
Chinese name: PPI-2458
English name: Beloranib
CAS:431077-35-9
Molecular formula: C22H36N2O6
Molecular weight: 424.53
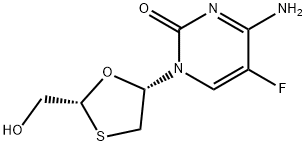
Chinese name: Nqutabin
English name: Emtricitabine
CAS:143491-57-0
Molecular formula: C8H10FN3O3S
Molecular weight: 247.25
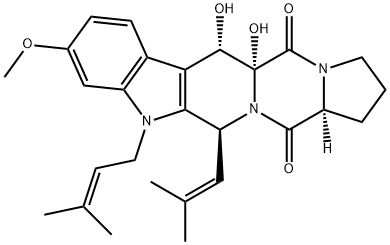
Chinese name: Aspergillus fumigatus toxin B
English name: Fumitremorgin B
CAS:12626-17-4
Molecular formula: C27H33N3O5
Molecular weight: 479.57